N. Madysa, V. Kain, R. Alemany Fernandez, N. Biancacci, B. Goddard, F. M. Velotti
CERN
13th Particle Accelerator Conference
Abstract
High intensities in the Low Energy Ion Ring (LEIR) at CERN are achieved by stacking several multi-turn injec- tions from the pre-accelerator Linac3. Up to seven consec- utive 200 μs long, 200 ms spaced pulses are injected from Linac3 into LEIR. Two inclined septa, one magnetic and one electrostatic, combined with a collapsing horizontal or- bit bump allows a 6-D phase space painting via a linearly ramped mean momentum along the Linac3 pulse and in- jection at high dispersion. The already circulating beam is cooled and dragged longitudinally via electron cooling (e- cooling) into a stacking momentum to free space for the fol- lowing injections. For optimal intensity accumulation, the electron energy and trajectory need to match the ion energy and orbit at the e-cooler section.
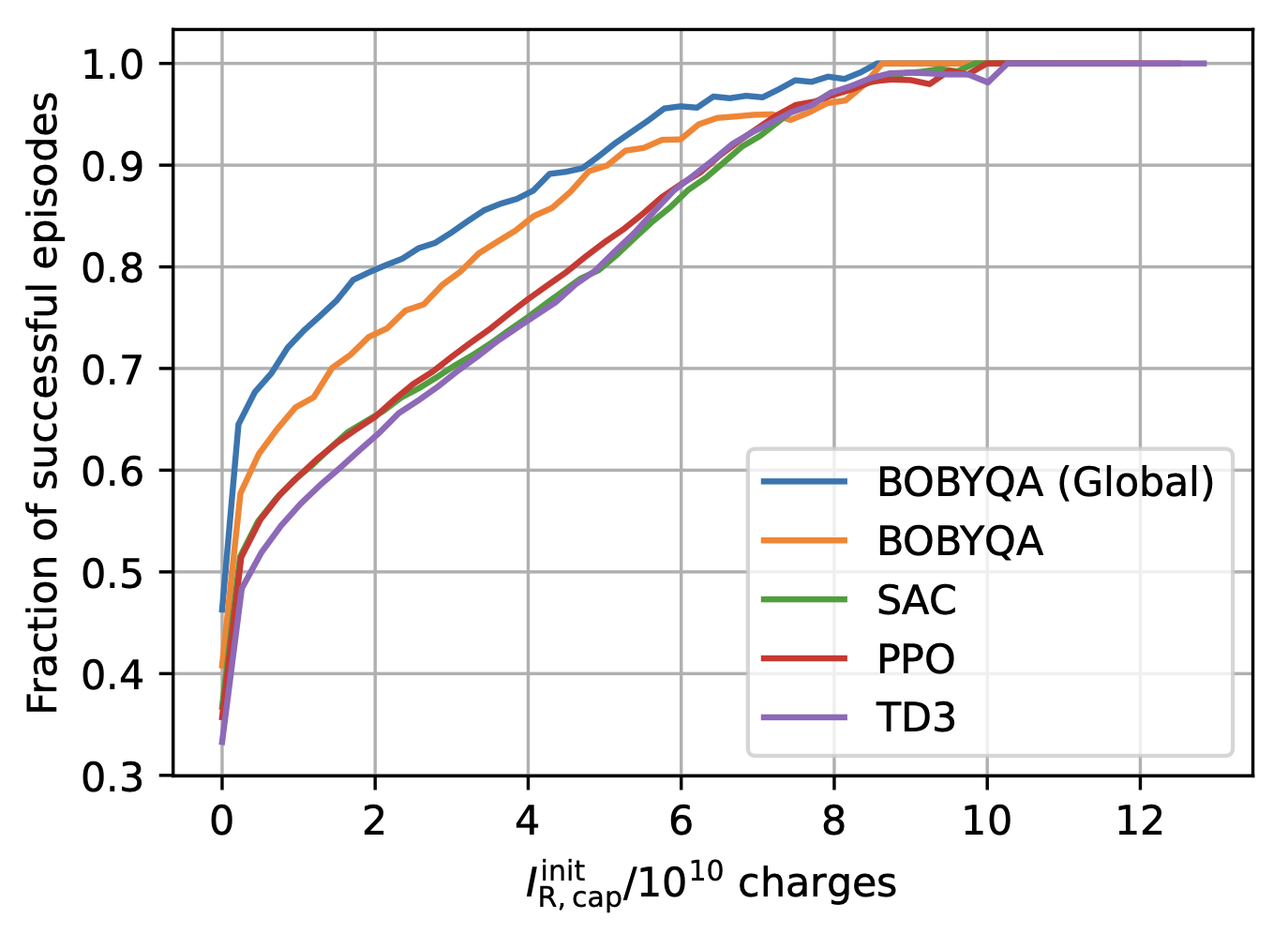
In this paper, a reinforcement learning (RL) agent is trained to adjust various e-cooler and Linac3 parameters to maximise the intensity at the end of the injection plateau. Variational Auto-Encoders (VAE) are used to compress lon- gitudinal Schottky spectra into a compact latent space rep- resentation as state input for the RL agent. The RL agent is pre-trained on a surrogate model of the LEIR e-cooling dynamics, which in turn is learned from the data collected for the training of the VAE. The performance of the VAE, the surrogate model, and the RL agent is investigated in this paper. An overview of planned tests in the upcoming LEIR runs is given.
Read the paper: https://jacow.org/ipac2022/papers/tupost040.pdf
Contact: Nico Madysa