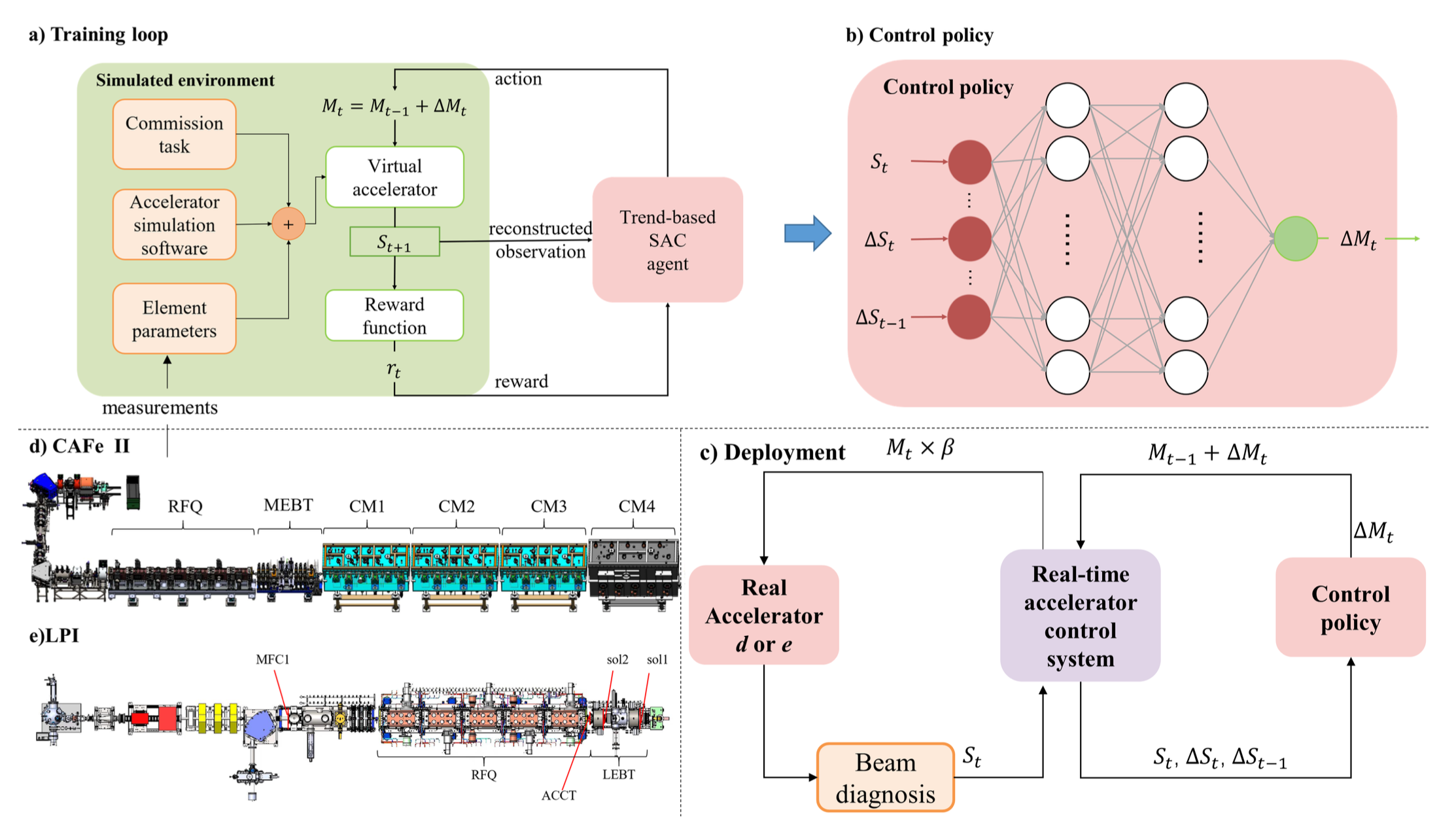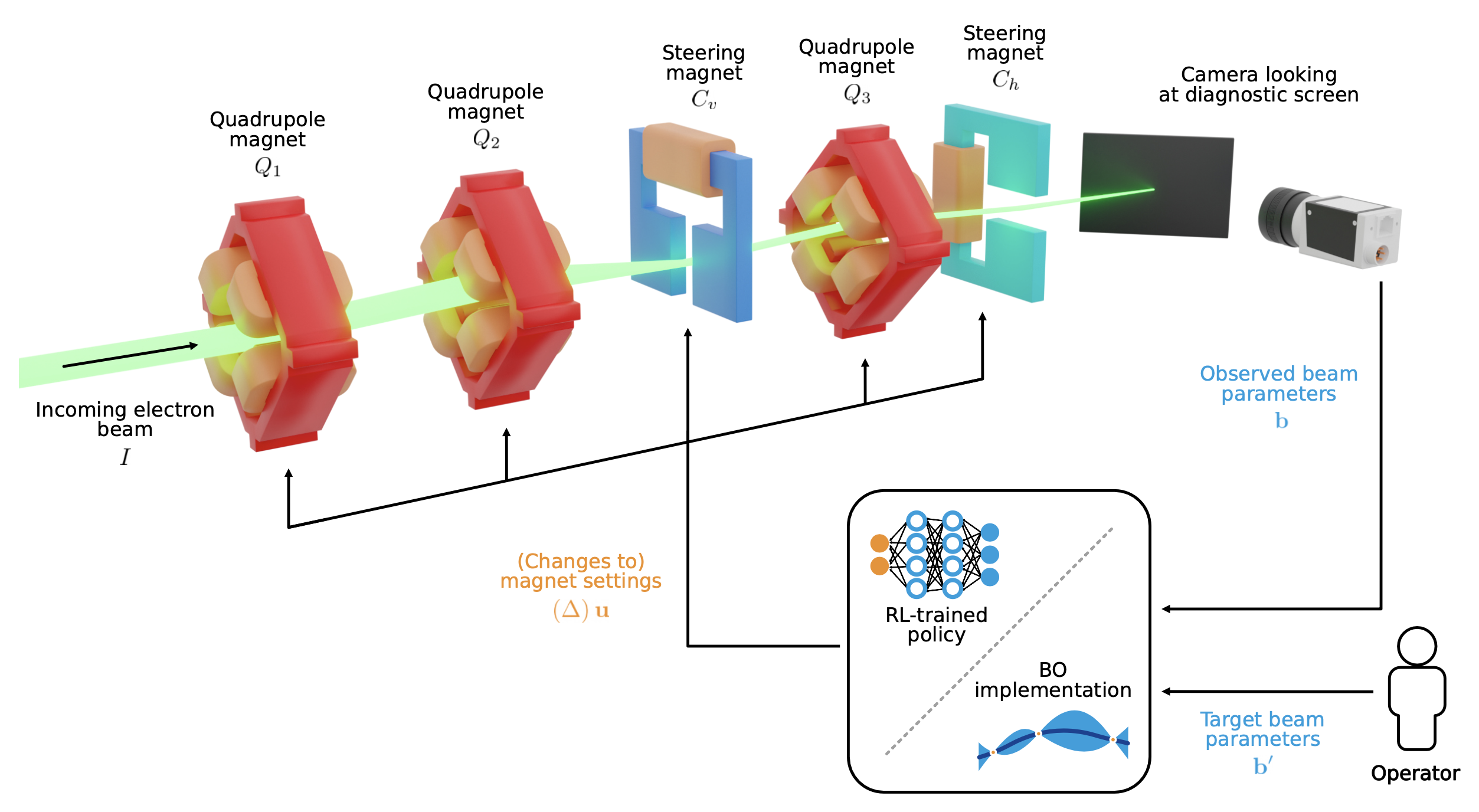
Learning to Do or Learning While Doing: Reinforcement Learning and Bayesian Optimisation for Online Continuous Tuning
J. Kaiser1, C. Xu2, A. Eichler1, A. Santamaria Garcia2, O. Stein1, E. Bründermann2, W. Kuropka1, H. Dinter1, F. Mayet1, T. Vinatier1, F. Burkart1, H. Schlarb1 1Deutsches Elektronen-Synchrotron DESY, 2 Karlsruhe Institute of Technology KIT arXiv Abstract Online tuning of real-world plants is a complex optimisation problem that continues to require manual intervention by experienced human operators. Autonomous tuning is a rapidly expanding field of research, where learning-based methods, such as Reinforcement Learning-trained Optimisation (RLO) and Bayesian optimisation (BO), hold great promise for achieving outstanding plant performance and reducing tuning times. Which algorithm to choose in different scenarios, however, remains an open question. Here we present a comparative study using a routine task in a real particle accelerator as an example, showing that RLO generally outperforms BO, but is not always the best choice. Based on the study’s results, we provide a clear set of criteria to guide the choice of algorithm for a given tuning task. These can ease the adoption of learning-based autonomous tuning solutions to the operation of complex real-world plants, ultimately improving the availability and pushing the limits of operability of these facilities, thereby enabling scientific and engineering advancements. ...