Towards automatic setup of 18 MeV electron beamline using machine learning
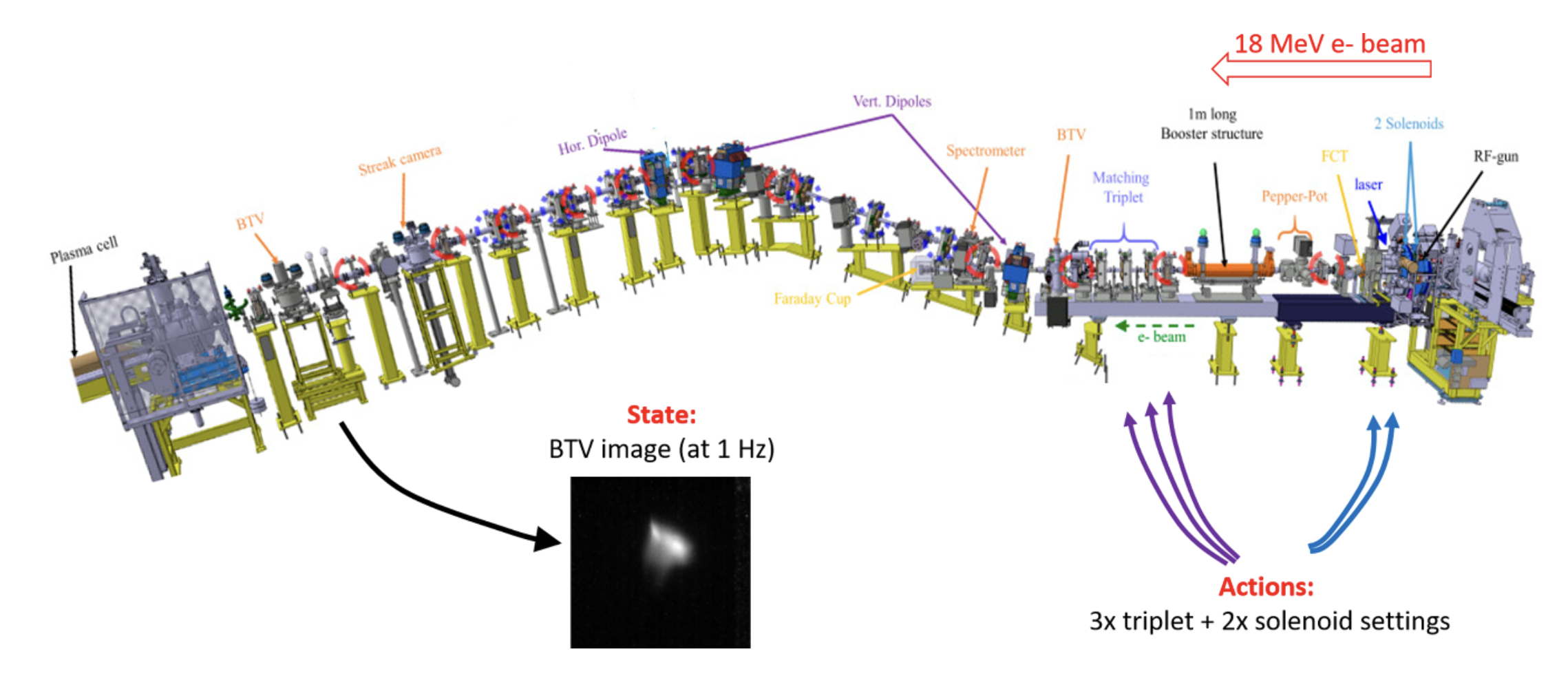
F. M. Velotti1, B. Goddard1, V. Kain1, R. Ramjiawan1, G. Z. Della Porta1 and S. Hirlaender2 1CERN, 2University of Salzburg Machine Learning: Science and Technology Abstract To improve the performance-critical stability and brightness of the electron bunch at injection into the proton-driven plasma wakefield at the AWAKE CERN experiment, automation approaches based on unsupervised machine learning (ML) were developed and deployed. Numerical optimisers were tested together with different model-free reinforcement learning (RL) agents. In order to avoid any bias, RL agents have been trained also using a completely unsupervised state encoding using auto-encoders. To aid hyper-parameter selection, a full synthetic model of the beamline was constructed using a variational auto-encoder trained to generate surrogate data from equipment settings. This paper describes the novel approaches based on deep learning and RL to aid the automatic setup of a low energy line, as the one used to deliver beam to the AWAKE facility. The results obtained with the different ML approaches, including automatic unsupervised feature extraction from images using computer vision are presented. The prospects for operational deployment and wider applicability are discussed. ...
