Ultra fast reinforcement learning demonstrated at CERN AWAKE
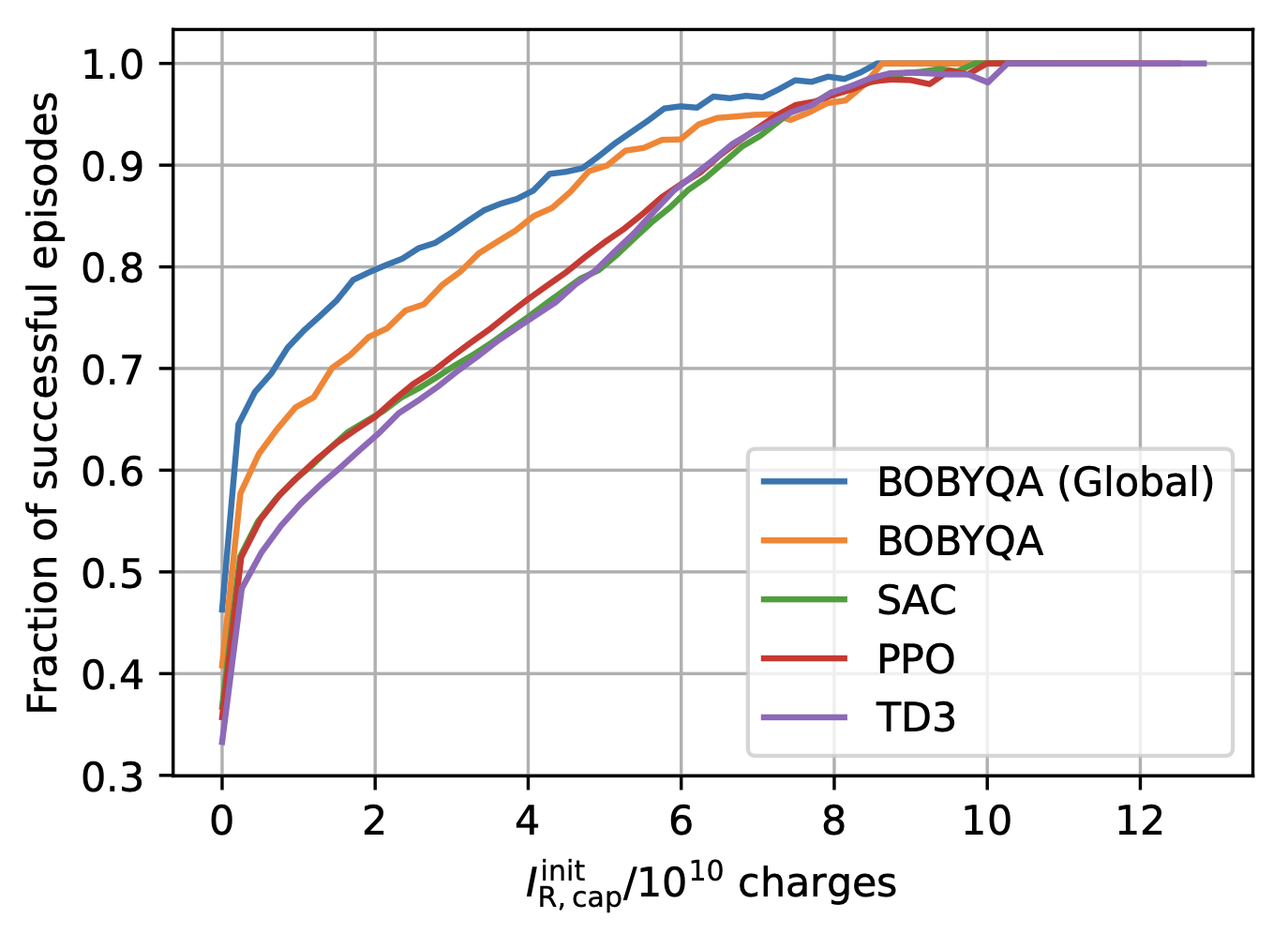
** Simon Hirlaender, Lukas Lamminger, Giovanni Zevi Della Porta, Verena Kain** Abstract Reinforcement learning (RL) is a promising direction in machine learning for the control and optimisation of particle accelerators since it learns directly from experience without needing a model a-priori. However, RL generally suffers from low sample efficiency and thus training from scracth on the machine is often not an option. RL agents are usually trained or pre-tuned on simulators and then transferred to the real environment. In this work we propose a model-based RL approach based on Gaussian processes (GPs) to overcome the sample efficiency limitation. Our RL agent was able to learn to control the trajectory at the CERN AWAKE (Advanced Wakefield Experiment) facility, a problem of 10 degrees of freedom, within a few interactions only. To date, numerical optimises are used to restore or increase and stabilise the performance of accelerators. A major drawback is that they must explore the optimisation space each time they are applied. Our RL approach learns as quickly as numerical optimisers for one optimisation run, but can be used afterwards as single-shot or few-shot controllers. Furthermore, it can also handle safety and time-varying systems and can be used for the online stabilisation of accelerator operation.This approach opens a new avenue for the application of RL in accelerator control and brings it into the realm of everyday applications. ...