Test of Machine Learning at the CERN LINAC4
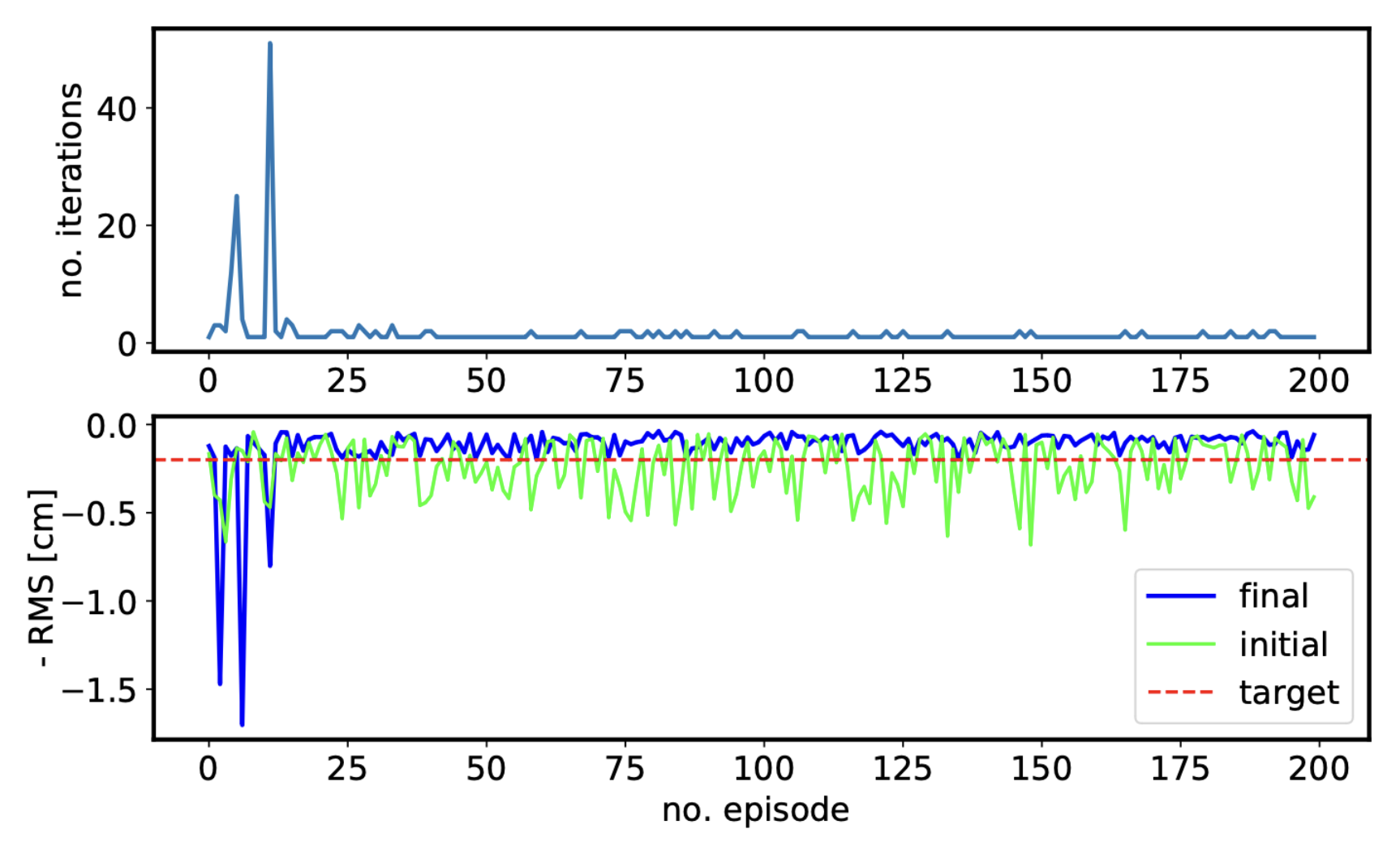
V. Kain1, N. Bruchon1, S. Hirlander1, N. Madysa1, I. Vojskovic1, P. Skowronski1, G. Valentino2 1CERN, 2University of Malta 61st ICFA ABDW on High-Intensity and High-Brightness Hadron Beams Abstract The CERN H−linear accelerator, LINAC4, served as atest bed for advanced algorithms during the CERN LongShutdown 2 in the years 2019/20. One of the main goals wasto show that reinforcement learning with all its benefits canbe used as a replacement for numerical optimization and asa complement to classical control in the accelerator controlcontext. Many of the algorithms used were prepared before-hand at the electron line of the AWAKE facility to makethe best use of the limited time available at LINAC4. Anoverview of the algorithms and concepts tested at LINAC4and AWAKE will be given and the results discussed. ...
